This guide is applicable not only to CentOS but also to other distributions like Ubuntu and Debian, as drivers are generally universal.
To install the Intel AC 3165NGW wireless network card driver on a CentOS system, you can follow these steps:
1. Update the System
First, ensure that your system is up to date to avoid potential dependency issues.
|
|
2. Install Necessary Development Tools and Dependencies
Install the development tools and kernel header files needed to compile the driver:
|
|
3. Check if the Wireless Network Card is Recognized by the System
Use the lspci or lsusb command to check if the wireless network card has been recognized by the system, and make a note of the specific model information.
|
|
Or, if it’s a USB wireless card:
|
|
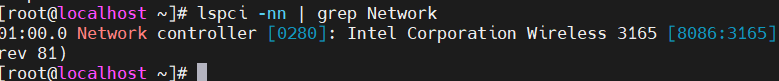
4. Obtain the Driver
For the Intel AC 3165, you’ll need to download the appropriate Linux driver from Intel’s official website or another reliable source. Typically, the official Intel driver is iwlwifi, which supports multiple wireless card models, including the AC 3165.
Visit the Intel Wireless Downloads page to find and download the latest driver corresponding to your network card. Address: https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/support/articles/000005511/wireless
5. Install the Driver
After downloading the driver, unpack it and follow the instructions provided in the README file. Note that some downloads might be in the form of firmware files (ending with .ucode), while others may require compiling from source.
Case 1: Downloaded as .ucode Firmware
If you download and unpack the Intel wireless card driver file and find only .ucode files (e.g., iwlwifi-7265-14.ucode), it means you have obtained firmware files rather than the source code for the driver. These .ucode files are binary firmware images used by the kernel’s iwlwifi driver, and they need to be placed correctly in the firmware directory of the system.
The steps to install the firmware files into the system are as follows:
- Determine the firmware storage location: Generally, Linux systems load wireless card firmware from the
/lib/firmwaredirectory. You need to place the.ucodefiles in this directory. - Copy the firmware files: Using root access or through sudo, copy the unpacked
.ucodefiles to the correct directory:If your system has a specific version folder (for example,1sudo cp iwlwifi-7265-14.ucode /lib/firmware//lib/firmware/iwlwifi), ensure you place the files in the corresponding subdirectory. - Update the firmware cache: In some distributions, it may be necessary to update the firmware cache (if applicable). However, in most modern Linux distributions, this step is usually not required.
- Reboot the system: To apply the changes, restart your system. After rebooting, the kernel should automatically detect and use the newly copied firmware files.
- Verify the installation: After the reboot, you can check the status of the wireless card using commands such as
ip linkoriwconfigto confirm that the wireless interface (likewlan0) is present and has no error messages.
If the wireless still does not function properly, check the system logs (using the dmesg command) for any possible error messages, which can help diagnose the problem. Additionally, ensure that your kernel supports the iwlwifi driver and that the module is correctly loaded. If the driver module is missing, you may need to install it through other means, such as using the distribution’s package manager (like yum or dnf in CentOS/RHEL) to install iwlwifi-dvm or related kernel module packages.
Case 2: Downloaded as Driver Source Code
If you have the driver source code instead, the general process involves the following steps:
|
|
6. Load the Driver Module
After installing the driver, you need to load the driver module. Typically, it will be automatically loaded after a reboot, but you can also load it manually:
|
|
Enable Wireless Network
First, ensure that the wireless network is enabled. You can use the following command to activate the wireless interface (assuming the wireless card is named wlan0):
|
|
Or, in newer systems, you might need to use the ip command:
|
|
Configure the Wireless Network
Manual Configuration:
-
Enable the wireless interface:
1sudo ip link set wlpXsY upReplace
wlpXsYwith the actual name of your wireless card. -
Scan for wireless networks:
1sudo iwlist wlpXsY scan -
Manually create a connection configuration:
If not using NetworkManager, you can create a configuration file (e.g.,/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-wlpXsY):1 2 3 4 5 6DEVICE=wlpXsY BOOTPROTO=dhcp ONBOOT=yes TYPE=Wireless ESSID=YourSSID MODE=ManagedAfter saving, activate the interface:
1sudo ifup wlpXsY
Using NetworkManager Configuration:
It’s recommended to use NetworkManager, as it provides a more convenient graphical interface and command-line tools like nmcli for network management.
|
|
Step 4: Verify the Network Connection
|
|
If you followed the steps correctly, you should have successfully installed the Intel 3165NGW wireless network card driver and configured your wireless network connection. If you encounter any issues, checking system logs (journalctl -u NetworkManager, dmesg) may provide useful debugging information.
Notes
- Before executing the above steps, ensure you have sufficient permissions and a basic understanding of system operations.
- Specific versions of CentOS may require particular versions of the driver, so be sure to confirm compatibility.
- If issues arise, checking system logs (like
dmesgoutput) might provide error messages that can assist in diagnosing problems. - Consider using DKMS (Dynamic Kernel Module Support) to manage driver modules so that they can be automatically rebuilt when the kernel is upgraded, maintaining driver compatibility.
