When attempting to run a sh script, if you see the error message ‘/bin/bash^M: bad interpreter: Text file busy’, it’s typically caused by differences in line endings between Windows and Unix/Linux operating systems.

In Windows, the end of each line is usually represented by “\r\n” (also known as CRLF). In contrast, Unix/Linux systems typically use just “\n” (also known as LF) for line endings. Therefore, when transferring a script file with Windows-style line endings to Unix/Linux, you may encounter this type of error.
To resolve this issue, you can use the dos2unix command to convert the line endings in your script file to Unix style. You can install and use the dos2unix tool by executing the following commands in your terminal:
- For Ubuntu/Debian Linux:
|
|
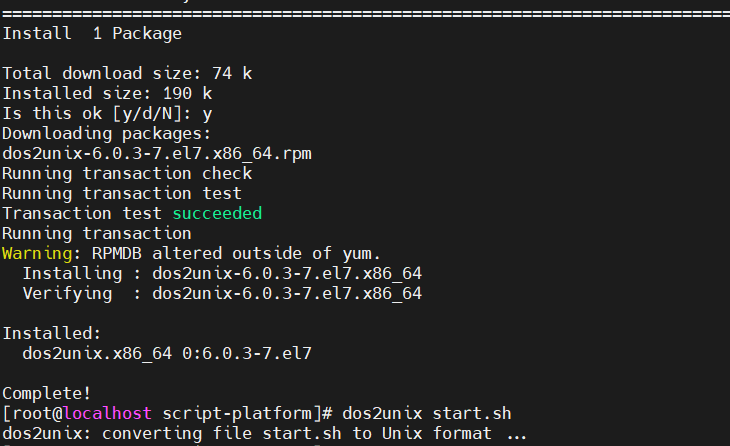
- For CentOS/RHEL Linux:
|
|
- For Mac OS X:
|
|
Once installed, you can convert the line endings in your script file to Unix style by using the following command:
|
|
After that, you can run your script again using ./start.sh to verify that the issue has been resolved.